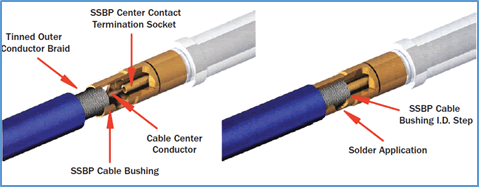
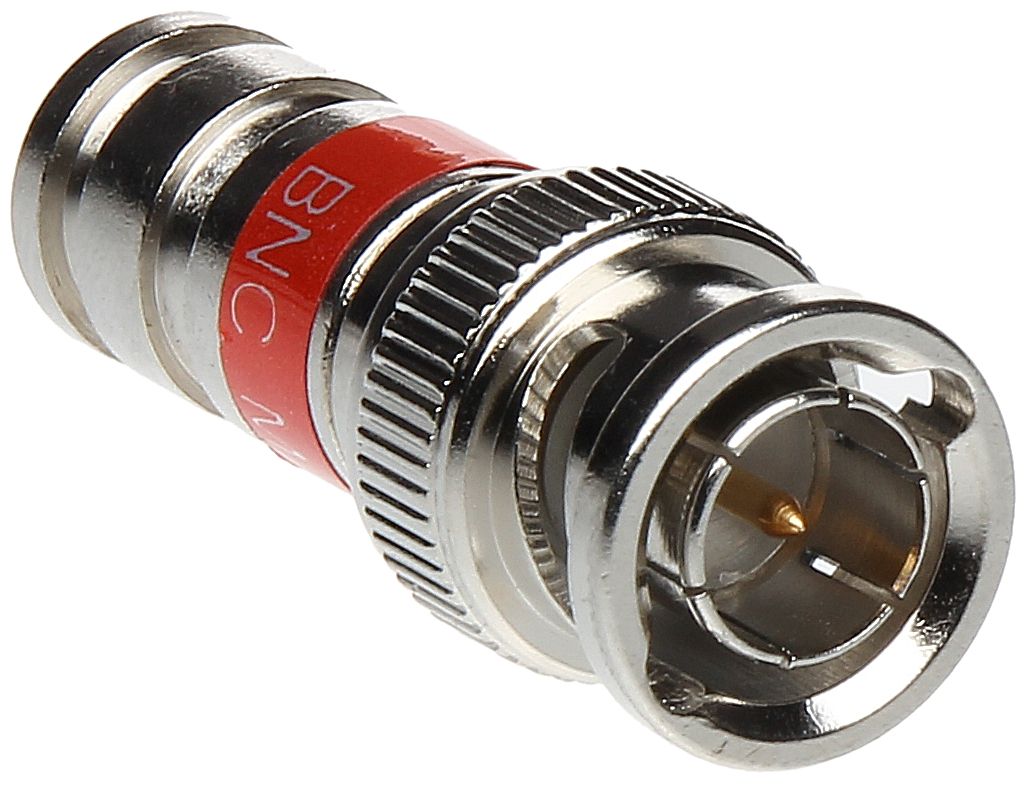
In the ever-evolving world of wireless communication, RF (radio frequency) connectors play a crucial role in ensuring reliable and efficient signal transmission. Whether you’re a professional in the telecommunications industry, an amateur radio enthusiast, or simply someone looking to optimize their home entertainment system, understanding the different types of RF connectors, their applications, and how to select and install them properly is essential. This comprehensive guide aims to provide you with the knowledge and insights you need to make informed decisions when working with RF connectors.
Types of RF Connectors
RF connectors come in various shapes and sizes, each designed to meet specific requirements and applications. Here are some of the most common types:
BNC Connectors
BNC (Bayonet Neill-Concelman) connectors are widely used in radio and television broadcasting, as well as in test and measurement equipment. They are known for their durability and ease of use, making them a popular choice for various applications.

SMA Connectors
SMA (SubMiniature version A) connectors are smaller and more compact than BNC connectors, making them ideal for applications where space is limited, such as in mobile devices and wireless communication systems. They are available in different versions, including straight and right-angle configurations.
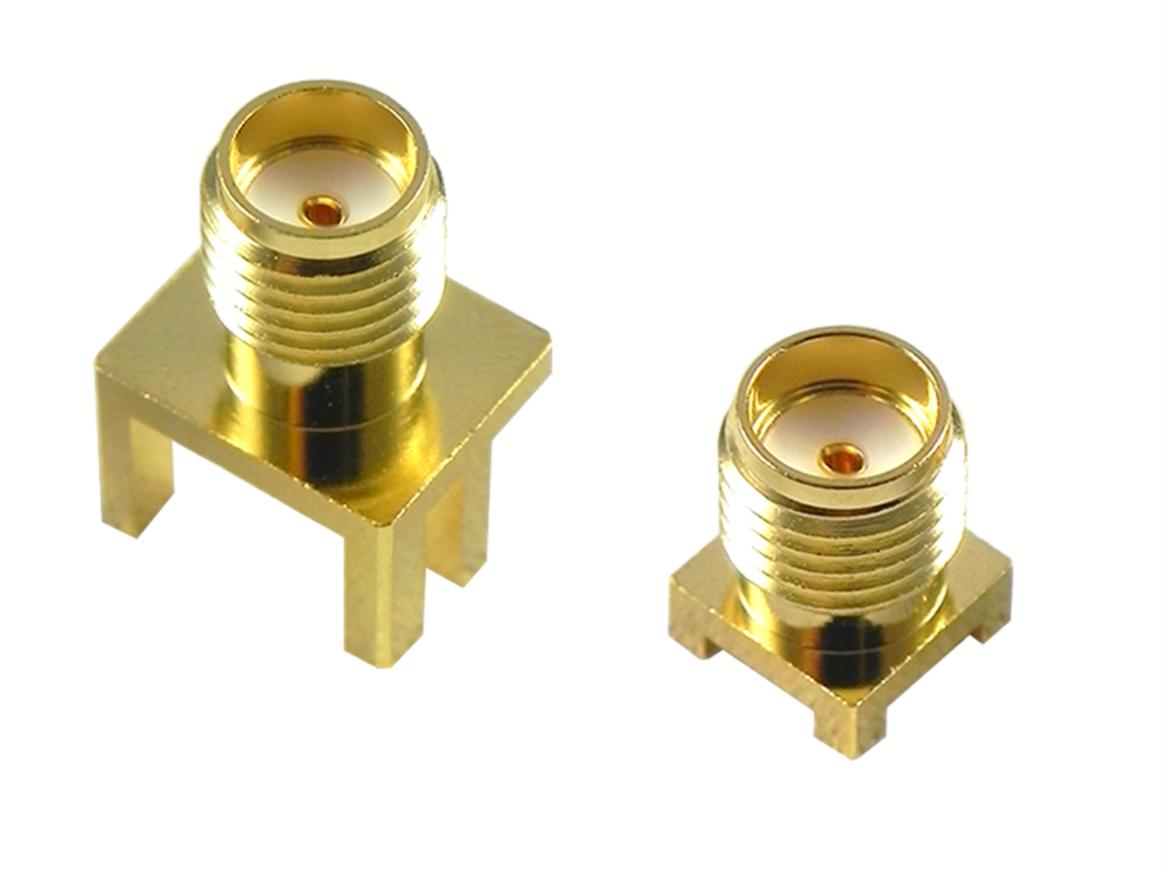

N-Type Connectors
N-Type connectors are known for their excellent electrical performance and ability to handle high frequencies, making them suitable for applications in the microwave and millimeter-wave frequency ranges. They are commonly used in wireless communication systems, satellite communications, and radar systems.
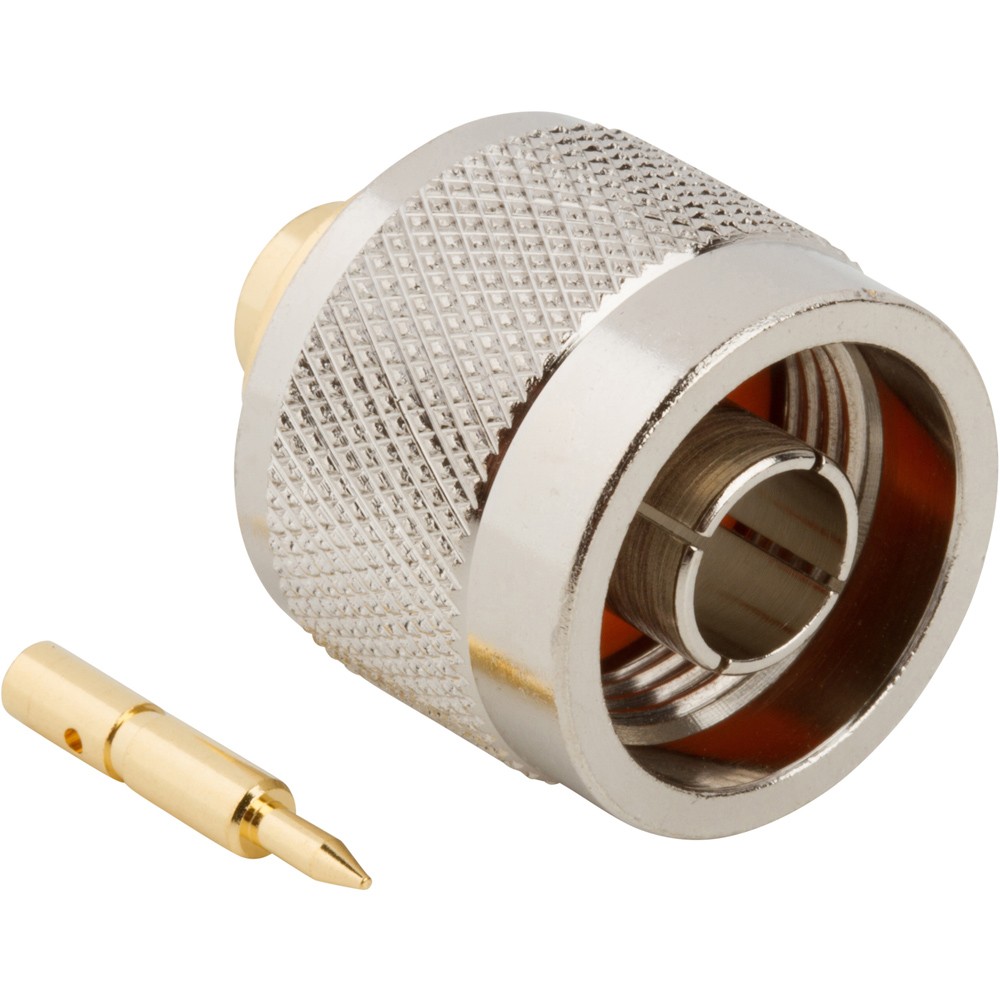

TNC Connectors
TNC (Threaded Neill-Concelman) connectors are similar to BNC connectors but feature a threaded coupling mechanism, providing a more secure and robust connection. They are often used in applications where vibration or shock is a concern, such as in mobile and outdoor environments.

These are just a few examples of the many types of RF connectors available. Each connector type has its own unique characteristics and is designed for specific applications and environments.
Applications of RF Connectors
RF connectors are used in a wide range of applications across various industries, including:
- Telecommunications: RF connectors are essential components in cellular networks, wireless internet systems, and satellite communications.
- Broadcasting: Radio and television broadcasting rely on RF connectors to transmit signals from studios to transmitters and antennas.
- Test and Measurement: RF connectors are used in various test and measurement equipment, such as spectrum analyzers, signal generators, and network analyzers.
- Military and Aerospace: RF connectors are used in radar systems, avionics, and other military and aerospace applications where reliable and secure signal transmission is critical.
- Automotive: RF connectors are used in various automotive systems, such as keyless entry, tire pressure monitoring, and vehicle-to-vehicle communication.
- Medical: RF connectors are used in medical equipment, such as MRI machines and patient monitoring systems.
The specific type of RF connector used in each application depends on factors such as frequency range, power handling capability, and environmental conditions.
Selection Factors for RF Connectors
When selecting the appropriate RF connector for your application, there are several factors to consider:
- Frequency Range: Different RF connectors are designed to operate within specific frequency ranges. It’s essential to choose a connector that can handle the frequencies you plan to use in your application.
- Impedance: RF connectors are designed to match specific impedance values, typically 50 or 75 ohms. Ensuring that the connector’s impedance matches the rest of your system is crucial for optimal signal transmission and minimizing reflections.
- Power Handling Capability: RF connectors have varying power handling capabilities, which is an important consideration for high-power applications such as broadcasting or radar systems.
- Environmental Conditions: The operating environment can significantly impact the performance and durability of RF connectors. Factors such as temperature, humidity, vibration, and exposure to chemicals should be taken into account when selecting the appropriate connector type.
- Size and Weight: In applications where space and weight are limited, such as in mobile devices or aerospace systems, smaller and lighter RF connectors may be preferred.
- Ease of Installation and Maintenance: Some RF connectors are easier to install and maintain than others, which can be an important consideration, especially in applications where frequent connections and disconnections are required.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can ensure that you select the most suitable RF connector for your specific application, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
Installation and Assembly
Proper installation and assembly of RF connectors are crucial for ensuring reliable signal transmission and preventing signal loss or interference. Here are some general guidelines for installing and assembling RF connectors:
- Preparation: Before installing the connector, ensure that the cable and connector surfaces are clean and free from debris or contaminants. Use appropriate cleaning solutions and tools to prepare the surfaces.
- Cable Stripping: Carefully strip the cable to the recommended length, taking care not to damage the inner conductor or dielectric material.
- Connector Assembly: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for assembling the connector onto the cable. This may involve crimping, soldering, or using specialized tools.
- Torquing: Many RF connectors require specific torque values to be applied during installation. Refer to the manufacturer’s specifications and use a torque wrench to ensure proper tightening.
- Weatherproofing: For outdoor or harsh environment applications, consider using weatherproofing materials, such as heat-shrink tubing or self-amalgamating tape, to protect the connector and cable from environmental factors.
- Testing: After installation, it’s recommended to perform testing and verification to ensure proper signal transmission and integrity.
It’s important to note that different types of RF connectors may have specific installation procedures and requirements. Always refer to the manufacturer’s instructions and seek professional assistance if you are unsure about the installation process.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance
Even with proper installation, RF connectors can experience issues over time due to various factors, such as wear and tear, environmental exposure, or improper handling. Here are some common troubleshooting tips and maintenance practices:
- Visual Inspection: Regularly inspect the connectors for signs of damage, corrosion, or debris buildup. Replace any damaged or worn connectors as needed.
- Cleaning: Use appropriate cleaning solutions and tools to remove any dirt, grease, or contaminants from the connector surfaces. This can help prevent signal degradation and ensure proper mating.
- Tightening: Over time, connectors may become loose due to vibration or thermal cycling. Periodically check the tightness of the connectors and re-torque them if necessary, following the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Replacement: RF connectors have a finite lifespan and may need to be replaced after a certain number of mating cycles or years of service. Consult the manufacturer’s recommendations for replacement intervals.
- Environmental Protection: If operating in harsh environments, consider using protective covers or enclosures to shield the connectors from exposure to moisture, dust, or other environmental factors.
- Signal Testing: Regularly perform signal testing and measurements to identify any potential issues with signal transmission or interference. This can help detect problems early and prevent further degradation.
By following these troubleshooting and maintenance practices, you can ensure the longevity and optimal performance of your RF connectors, minimizing downtime and potential signal issues.
Conclusion
RF connectors are essential components in various wireless communication systems and applications. Understanding the different types of connectors, their applications, and the factors to consider when selecting and installing them is crucial for ensuring reliable and efficient signal transmission.
This comprehensive guide has provided you with valuable insights into the world of RF connectors, covering topics such as connector types, applications, selection factors, installation procedures, and troubleshooting tips. By applying the knowledge gained from this guide, you can make informed decisions and ensure that your RF systems operate at their best.
Remember, proper installation, maintenance, and adherence to industry standards are key to maximizing the performance and lifespan of your RF connectors. Don’t hesitate to seek professional assistance or consult with experts in the field if you encounter any challenges or have specific requirements.
Stay up-to-date with the latest advancements in RF technology and continue to expand your knowledge to stay ahead in this ever-evolving industry.