In the rapidly evolving landscape of digital entertainment, Internet Protocol Television (IPTV) has emerged as a revolutionary technology, reshaping how we consume video content. This article delves into the intricacies of IPTV, exploring its functionality, benefits, and market trends.
Understanding IPTV
IPTV stands for Internet Protocol Television, a system that delivers television content over Internet Protocol (IP) networks. Unlike traditional broadcast, cable, or satellite TV platforms, IPTV uses the internet to transmit video content directly to users’ devices.
Key Features of IPTV:
- Streams video content over a closed, private network
- Offers both live TV and on-demand programming
- Enables interactive features and personalized viewing experiences
How IPTV Works
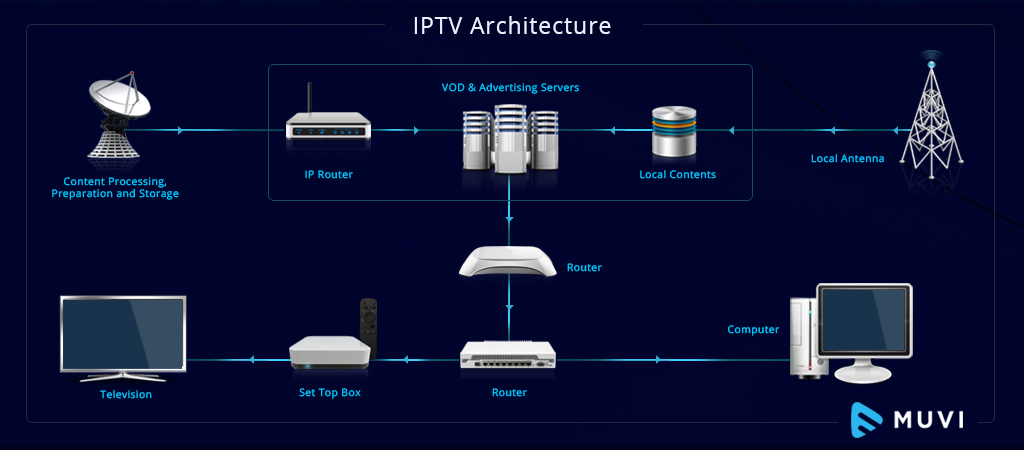
IPTV (Internet Protocol Television) operates on a sophisticated infrastructure that seamlessly integrates servers, networks, and user devices to deliver television content. The process involves several key stages:
Content Acquisition and Processing
- Source Reception: IPTV service providers receive programming from various TV stations and content providers, including:
- Live broadcasts
- Recorded shows
- Movies
- Optimization: The received video content undergoes encoding and compression to optimize it for internet transmission.
- This crucial step reduces file sizes while maintaining quality
- Enables efficient streaming
Storage and Distribution
Live Content
- Streamed directly to users in real-time
- Requires robust bandwidth and low latency for a smooth viewing experience
On-Demand Content
- Stored on servers for later access
- Requires efficient storage solutions and retrieval systems
Content Delivery
- Packet Creation: Video streams are divided into smaller data packets for transmission over the IP network.
- Transmission: These data packets are sent across the internet to reach end-users.
Benefits:
- More efficient use of bandwidth
- Enhanced stream reliability
User Reception
- Device Compatibility: Subscribers receive data packets on various devices:
- Smart TVs
- Computers
- Mobile devices
- Content Reassembly: A set-top box or dedicated application reassembles the packets into viewable content.
- Ensures high-quality video without interruptions
Types of IPTV Services
IPTV providers typically offer three main types of services:
- Live Television: Real-time broadcasting of TV channels.
- Video on Demand (VoD): A library of content users can access at any time.
- Time-Shifted Media: Allows users to replay TV programs that have already been broadcast.
Market Trends and Growth
The IPTV market is experiencing significant growth:
- Market Size: Expected to grow from $138.81 billion in 2023 to $162.37 billion in 2024.
- Projected Growth: Forecasted to reach $305.16 billion by 2028.
- CAGR: Anticipated Compound Annual Growth Rate of 17.0
Factors Driving Growth:
- Increasing internet penetration globally
- Rising adoption of smart devices
- Growing demand for on-demand content
Benefits of IPTV
- Flexibility: Watch content on various devices, anytime, anywhere.
- Interactivity: Pause, rewind, or fast-forward live TV; access interactive apps and services.
- Personalization: Tailored content recommendations and customized viewing experiences.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Often more affordable than traditional cable or satellite packages.
Legal Considerations
While IPTV technology itself is legal, some services operate in a gray area:
- Licensed Services: Many telecom companies and streaming platforms offer legal IPTV services.
- Unauthorized Streaming: Some providers may offer copyrighted content without proper licensing, which can be illegal.
Tip: Always ensure you’re using a reputable, licensed IPTV service to avoid legal issues.
The Future of IPTV
As technology continues to advance, we can expect:
- Enhanced integration with 5G networks for improved mobile viewing
- Increased use of AI for content recommendations and personalization
- Further convergence with other smart home technologies
Conclusion
IPTV represents a significant shift in how we consume television and video content. With its flexibility, interactivity, and growing market presence, IPTV is poised to play an increasingly important role in the future of entertainment. As consumers, understanding this technology allows us to make informed decisions about our viewing habits and choose services that best meet our needs.
IPTV itself is a legal technology, but some IPTV services may offer unauthorized content. Always choose a reputable IPTV provider to ensure you’re accessing legal content.
Many smart TVs, computers, and mobile devices are compatible with IPTV. However, some services may require a specific set-top box or streaming device.
Most IPTV services offer cloud-based recording, allowing you to record and store your favorite shows without the need for a physical DVR.
For smooth IPTV streaming, a minimum internet speed of 10 Mbps is recommended. However, for the best experience, especially with HD or 4K content, aim for speeds of 25 Mbps or higher.