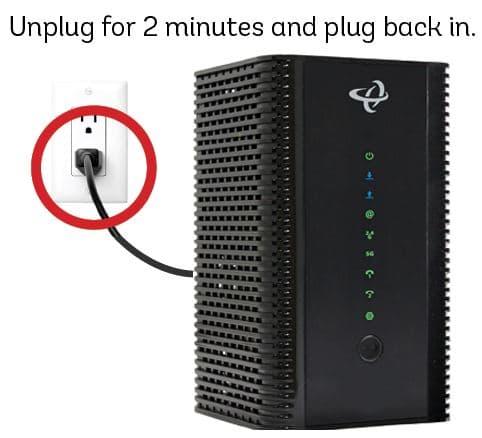
In my years as a network technician, I’ve encountered a myriad of connectivity issues. One of the most common and vexing error messages is “A network cable is not properly plugged in or may be broken.” This seemingly innocuous problem can bring an entire network to its knees, wreaking havoc on productivity and causing frustration for both IT professionals and end-users alike.
In this comprehensive guide, I’ll walk you through the most effective steps to diagnose and resolve network cable issues. We’ll cover everything from basic checks to advanced solutions, drawing on my extensive hands-on experience in the field.
Decoding the Error Message
Before we delve into solutions, it’s crucial to understand what this error message actually signifies. When your computer displays “A network cable is not properly plugged in or may be broken,” it’s indicating a physical problem with the network connection. This could stem from several issues:
- A physically disconnected cable
- A damaged or faulty cable
- A problem with the network port on your device or router
- An outdated or corrupted network adapter driver
Now that we’ve identified potential causes, let’s explore how to diagnose and address them.
Essential Troubleshooting Steps
1. Verify Physical Connections
The first and most obvious step is to ensure all cables are properly connected. You’d be surprised how often I’ve resolved network issues simply by re-seating a loose cable. Here’s what to check:
- Confirm that the Ethernet cable is securely plugged into both your device and the router/switch.
- If you’re using a laptop docking station, ensure it’s properly connected.
- Inspect the cable for any visible damage or kinks.
2. Examine the Cable for Damage
Carefully inspect the entire length of the cable for any signs of wear or damage. Look out for:
- Frayed or exposed wires
- Sharp bends or kinks
- Cuts or tears in the outer jacket
If you spot any damage, it’s best to replace the cable entirely. In my experience, attempting to repair damaged Ethernet cables often leads to intermittent connectivity issues down the road.
3. Test an Alternative Port
If the cable appears to be in good condition, try plugging it into a different port on your router or switch. This can help isolate whether the issue lies with the cable itself or the network hardware.
4. Swap with a Known Working Cable
One of the quickest ways to determine if the cable is at fault is to replace it with a known working cable. If the new cable resolves the issue, you’ve identified the culprit.
Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques
If the basic steps don’t resolve the issue, it’s time to dig deeper. Here are some more advanced troubleshooting techniques I’ve found effective over the years:
1. Update Network Adapter Drivers
Outdated or corrupted network adapter drivers can sometimes cause connectivity issues. To update your drivers:
- Open Device Manager (press Windows key + X, then select “Device Manager”)
- Expand the “Network adapters” section
- Right-click on your network adapter and select “Update driver”
- Choose “Search automatically for updated driver software”
If Windows doesn’t find a new driver, visit the manufacturer’s website to download and install the latest version manually.
2. Run Windows Network Troubleshooter
Windows has a built-in network troubleshooter that can often identify and fix common issues automatically. To run it:
- Navigate to Settings > Network & Internet > Status
- Click on “Network troubleshooter”
- Follow the on-screen instructions
While not always successful, I’ve seen this tool resolve many simple network problems without further intervention.
3. Reset TCP/IP Stack
Resetting the TCP/IP stack can often resolve stubborn network issues. To do this:
- Open Command Prompt as an administrator
- Type the following commands, pressing Enter after each:
netsh winsock reset
netsh int ip reset
ipconfig /release
ipconfig /renew
ipconfig /flushdns- Restart your computer
This process resets your network settings to their default state, which can often clear up connectivity problems.
4. Check for IP Address Conflicts
Sometimes, IP address conflicts can cause network issues that mimic cable problems. To check for conflicts:
- Open Command Prompt
- Type
ipconfig /alland press Enter - Look for any entries that say “IP Address” and “Duplicate”
If you find a conflict, try releasing and renewing your IP address using the ipconfig /release and ipconfig /renew commands.
Preventing Future Issues
As the adage goes, an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure. Here are some tips to help prevent network cable issues in the future:
- Invest in high-quality cables: Opt for reputable, well-constructed Ethernet cables. In my experience, cheap cables are far more likely to fail or cause intermittent issues.
- Practice proper cable management: Avoid sharp bends, kinks, and stretching. Use cable ties or management systems to keep cables organized and protected.
- Perform regular maintenance: Periodically inspect your network cables for signs of wear or damage. Replace any cables that show signs of deterioration.
- Shield from environmental factors: Keep cables away from heat sources, direct sunlight, and areas with high foot traffic.
- Utilize cable testers: For larger networks, invest in a quality cable tester. This can help you quickly identify issues before they cause downtime.
When to Seek Professional Help
While many network cable issues can be resolved with the steps outlined above, there are times when it’s best to call in a professional. Consider seeking expert help if:
- You’ve exhausted all troubleshooting steps and the issue persists
- You’re dealing with a large, complex network
- You suspect there might be issues with your network infrastructure
- You’re not comfortable working with network hardware or software
As someone who’s been called in to fix “simple” issues that turned out to be much more complex, I can attest to the value of professional expertise in certain situations.
Conclusion
Network cable issues can be frustrating, but with a systematic approach to troubleshooting, most problems can be resolved swiftly. Remember to start with the basics – checking physical connections and cable integrity – before moving on to more advanced techniques.
By following the steps outlined in this guide, you’ll be well-equipped to diagnose and resolve most network cable issues. And remember, prevention is key. Regular maintenance and proper cable management can save you countless hours of troubleshooting in the long run.
If you’re still experiencing issues after trying these solutions, don’t hesitate to reach out to a professional. Sometimes, a fresh pair of eyes and specialized expertise can make all the difference in resolving stubborn network problems.
Stay connected, and happy networking!

![[Windows 8] How to share Internet connection with your phone, tablet, other computers, and other dev](https://www.800908.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/10/1224-6.png)

